Windows operating systems have been an important part of computers and technology for more than 30 years, changing the way we use them and how we connect with them. Windows has always changed to meet the needs of today’s tech-savvy world, from its simple start to the advanced and easy-to-use versions we use today.
Table of Contents
Windows Operating Systems 1.0: The First Step
The trip began in 1985, when Windows 1.0 came out. It was very basic compared to what we have now, but it was a big step away from the command-line interface and the beginning of the graphical user interface (GUI). At the time, the idea that users could move around in apps using a mouse was very new.
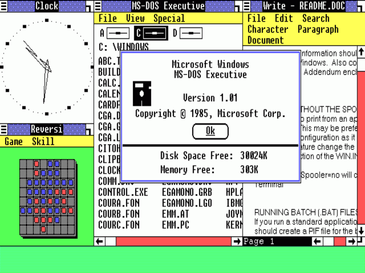
Features provided by Windows 1.0
- User Interface (GUI): Windows 1.0 was the first PC to have a graphical user interface (GUI), which lets users move around and connect with their system using a mouse.
- Multitasking: This version added some limited multitasking features that let users open more than one app at the same time. However, it wasn’t as effective as the multitasking tools used today.
- MS-DOS Executive: Windows 1.0 came with the MS-DOS Executive, which showed the file system visually and made it easier to work with files.
- Control Panel: The Control Panel was first introduced in Windows 1.0. It gives users a central place to change system settings and make their computer experience more personal.
- Painting and Notepad: Simple programs like Paint and Notepad were included so users could make simple images and text files.
- Clock, Calendar, and Calculator: Windows 1.0 came with basic utility programs like a clock, calendar, and calculator, which made the whole experience better for the user.
Windows 3.1: Getting Going
When Windows 3.1 launched in 1992, it underwent a lot of positive changes and received quick user adoption. The famous Start button was added, and the ability to use TrueType fonts made the interface look better. Windows 3.1 set the stage for the easy-to-use experience that has come to be associated with the Windows name.
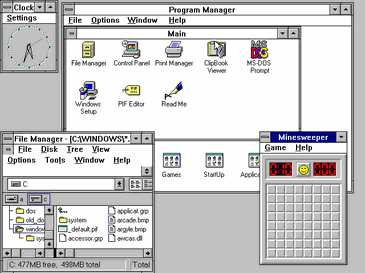
Feature provided by Windows 3.1
- Windows 3.1 had better support for multimedia devices like Sound Blaster and MIDI controllers. This sets the stage for better video and music experiences on Windows devices.
- Better Performance: Windows 3.1 improved system performance by making better use of system resources and running more smoothly than Windows 3.0’s predecessor.
- It has a program manager and a file manager. Users could easily organize and start up programs in the Program Manager, while the File Manager made it easier to find and handle files and folders.
- Better Print Manager: Windows 3.1’s Print Manager made it easier for users to handle and keep an eye on their printing jobs by making print job management better. This program lets you access 32-bit disks. With Windows 3.1, 32-bit disk access became possible. This made the file system run faster and made it easier to move data between the operating system and storage media.
- Better System Fonts: Adding flexible system fonts made all the text on the system easier to read and look better.
Windows 95 changed everything.
Windows 95 changed everything and made Microsoft a big name in the computer world. This version came out with a groundbreaking advertising campaign that featured the famous Start button. It also worked perfectly with the internet, bringing in a new age of online connection. The change to the graphics and the addition of the taskbar made Windows a well-known brand.

Feature Provided by Windows 95
- The “Start” button:When the Start menu came out, it gave users a central place to access apps, files, and settings, which made browsing easier.
- Multiple tasks: Better multitasking lets users run more than one app at the same time, which increases output and efficiency.
- Long Filenames: Windows 95 added support for long filenames, which let users make file names that are more informative and easy to remember.
- Web browser: Internet Explorer 1.0 came with Windows 95. It was Microsoft’s first web browser and a step toward better internet access.
- The Taskbar made it easy to switch between open programs and get to the Start menu, which improved the general user experience.
- Support for DirectX: The addition of DirectX made it easier for video programs and games to work together, which helped the PC gaming business grow.
- Network Support: Windows 95 came with built-in networking support that made it easier for users to connect to local area networks and share resources.
Windows XP: A Reliable Partner
When it came out in 2001, Windows XP was a big deal for security and usefulness. It’s a good choice for both home and business use because it’s easy to use and has better protection features. The fact that XP is still on the market well into the 2010s shows how popular it is.
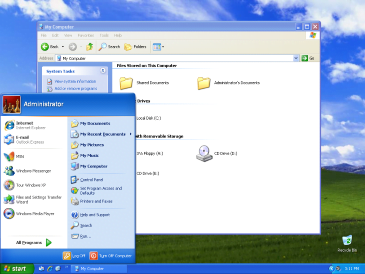
Feature Provided by Windows XP
- Stability and Longevity: Windows XP had the best stability and longevity of any operating system, making it a trusted choice for people all over the world well into the 2010s.
- Intuitive User Design: Windows XP sets a bar for ease of use with its intuitive and user-friendly design, which lets a lot of people use it.
- Better security measures: Windows XP made big changes to security, making it better at protecting against new threats than versions that came before it.
Windows 7: Finding the Right Balance
When it came out in 2009, Windows 7 was the right mix of good looks and good speed. The new Aero Glass style and toolbar made it look better, and the ability to do more than one thing at once and better security made it a hit with users. A lot of people still love Windows 7, even though official support for it stopped in 2020.

Feature Provided by Windows 7
- Aero Snap and Shake: The Aero Snap feature in Windows 7 makes it easy to arrange and compare open windows by snapping them to the screen’s edges or corners. Aero Shake also lets users focus on a single window by quickly shaking the current window and making other windows smaller. These features made it easier to switch between tasks and control windows.
- Library: Libraries were a new way to organize things that came with Windows 7. Libraries made it easier to organize papers, music, pictures, and videos by letting users combine files from different places into a single view. This made it easy for users to view and work with their material and made managing files easier.
- Better Taskbar: The taskbar got a makeover in Windows 7, with new features like Jump Lists and the option to “pin” apps. Jump lists made it easy to get to recent files and common jobs for each app, which made things run more smoothly. Users could change their desktop so that regularly used apps were easy to get to by “pinning” them. This made the user experience more streamlined.
Windows 8 and 8.1: Leaving and Coming Back
Because Windows 8’s design was built on tiles, it was different from standard desktops. Users were divided over its bold design, but Windows 8.1 tried to find a middle ground by adding the Start button back and making the OS easier to use. Even though some people didn’t like it at first, this version set the stage for later versions of Windows.

Features provided by Windows 8 and 8.1
- Start Screen and Live Tiles: Windows 8 got rid of the standard Start screen and replaced it with a Start Screen that has Live Tiles that change over time. Live Tiles let apps update you in real time, making the experience more engaging and flexible than static icons.
- Charms Bar to Make Navigation Easier: The Charms Bar was in Windows 8. To get to it, swipe or move the mouse to the right side of the screen.The Charms Bar made it easy to get to important features like Search, Share, Start, Devices, and Settings. It also made browsing easier and the user experience better overall.
- Snap View for Multitasking: Windows 8 added Snap View, which lets users do more than one thing at once by putting two apps next to each other on the screen. This function made people more productive by letting them work on multiple apps at once without having to switch between full-screen views
Windows 10: A Single System
When it came out in 2015, Windows 10 was a return to comfort while also keeping up with the latest computer trends. The Start menu came back with a bang, and Microsoft’s virtual helper Cortana was released. Windows 10 focused on a single environment, making it easy for devices to work together and providing regular patches to improve security and usefulness.

Features Provided by Windows 10
- Cortana Integration: Cortana is a virtual helper that came with Windows 10 and lets you use voice commands, ask natural language questions, and get personalized help. The goal of this merger was to give people a more dynamic and hands-free computer experience.
- Single-User Interface with Start Menu: After being absent in Windows 8, the Start menu was brought back in Windows 10. It combines the comfort of the original Start menu with the Live Tiles that were added in Windows 8. This mix gave people a unified interface that they could change to fit both standard PC and current app experiences.
- Continuum for Hybrid Devices: Windows 10 was made to be flexible, especially for devices that can be used as computers or tablets. With Continuum, the operating system could change its interface based on the state of the device. This made switching between touch-based and standard keyboard/mouse input smooth.
The Next Part of Windows 11
As of my most recent update in 2022, Windows 11 had a sleek and centered Start menu, smooth sides, and new features like Snap Layouts that made it easier to switch between tasks. This version kept up the trend of making the user experience smooth and nice to look at, with a focus on getting work done and working together.
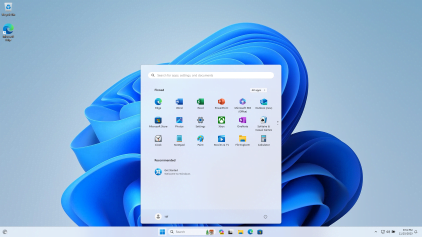
Features Provided by Windows 11
- Revamped Start Menu : Windows 11 introduces a centered Start Menu for a more streamlined and visually appealing user experience.
- Snap Layouts and Snap Groups : Enhanced multitasking with intuitive window organization for increased productivity
- Widgets for Personalized Information: Dynamic widgets provide at-a-glance access to personalized news, weather, and calendar updates
- Microsoft Teams Integration: Seamless integration of Microsoft Teams directly into the taskbar for effortless communication and collaboration.
- Redesigned Microsoft Store: A redesigned and optimized Microsoft Store with a diverse range of apps for a more immersive experience.
- Direct integration of Android Apps: Windows 11 allows users to run Android apps natively on their PCs.
- Snap Layouts and Snap Groups: Enhanced multitasking with intuitive window organization for increased productivity
- Virtual Desktops Overhaul: Virtual Desktops are more customizable and accessible, allowing users to create distinct workspaces.
- DirectStorage for Gaming: Faster game loading times and smoother experiences with DirectStorage technology.
- New Gaming Features with Auto HDR: Enhanced gaming visuals through Auto HDR support for a more immersive gaming experience.
Why do operating systems based on Windows stand out?
- User-Friendly Interface: Windows has always put an emphasis on making its systems easy for people who aren’t very tech-savvy to use.
- When it comes to flexibility, the Windows operating system is known for working with a wide range of hardware and software. This makes it a good choice for many devices and uses.
- Regular Updates: Microsoft promises to release updates on a regular basis, so users can get the newest features, security changes, and better speed.
- Support for apps: Windows is a popular operating system for both personal and business use, and its large library of suitable apps only makes that case.
In conclusion, the Windows operating system has changed a lot over the years. It has kept up with changes in technology while still focusing on user happiness. Each version has left its own mark on the digital world, which is one reason why Windows is still so popular with a wide range of users. As we look to the future, Windows keeps getting better, which means it will be an important part of digital life for many years to come.


